# Data Types and Nullability
In addition to showing basic structure of tables and their relationships, Entity Relationship Diagrams (ERDs) can also give us more insight into the columns. This can include data types for each column and whether a column can have null values. Let’s explore these concepts with an example diagram.
# College Courses Diagram
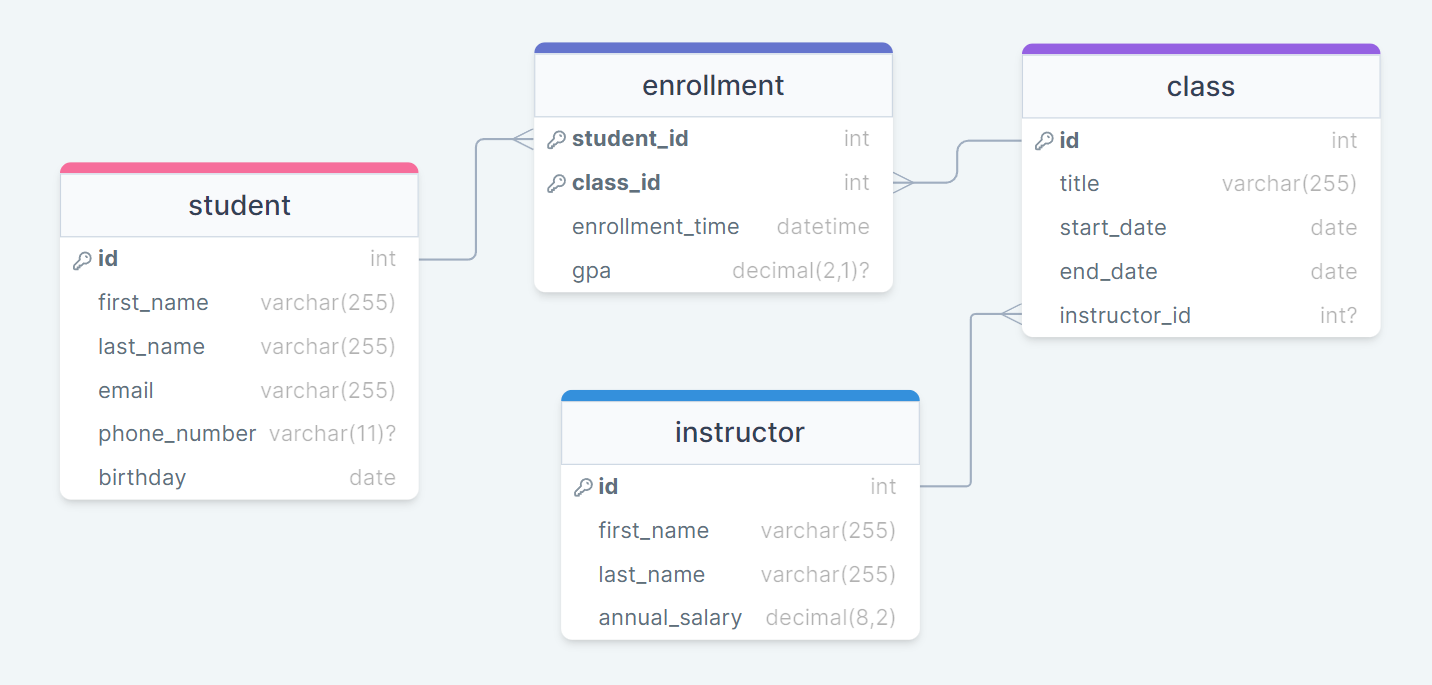
# Data Types
Each column in a table has a specific data type that dictates the kind of data it can hold to the right of its name. There are many different types but some of the most common are:
- Strings: These are sequences of characters like the words in a sentence. In SQL they are referred to as
VARCHAR(variable character). VARCHARs can be given a maximum number of characters that they can accept in parathesis. AVARCHAR(255)could hold 255 characters. - Datetimes: This type represents dates and times. The keyword is SQL is
DATETIME. - Integers: These are whole numbers. The keyword in SQL is
INT. - Decimals: These are numbers with a fractional part, such as currency or averages. Decimals are given two parameters, a size and a number of digits that can appear after the decimal point.
DECIMAL(4,2)could hold 4 total digits with two of those digits appearing after the decimal point. SoDECIMAL(4,2)could hold any value between -99.99 and 99.99.
A full list of data types can be found here at W3Schools: SQL Data Types for MySQL, SQL Server, and MS Access (w3schools.com)
# Nullability
In addition to data types, ERDs can indicate whether a column can have a null value. A null value represents the absence of a value. Whether a field can be null or not depends on the business rules and data requirements:
- Nullable Fields: These are optional and are marked with a question mark (
?) after the data type in this diagram. - Non-Nullable Fields: These are required and have no question mark.
Taking a look at the College Courses Diagram above, you’ll notice that each column in the tables has a defined data type. Some fields, like phone_number in the student table, are marked as nullable (indicated by varchar(11)?), meaning it is not mandatory for a record to have this information.
# Practice Questions
- Suppose we need to record the
office_locationfor eachinstructorin the College Courses Diagram. What data type should this column be and should it be allowed to be null? Why? - Imagine we want a
last_accessedcolumn in theenrollmenttable that tracks when a student last signed into their class on Canvas. What data type should this column be and should it be allowed to be null? Why?